- India | USA | South Africa | Australia | U.K
- info@cplflighttraining.com
- Opening : Mon-Sat 08:30 - 18:00
From Zero to Airline Entry: The Journey to Becoming a Pilot in India

Dreaming of a career in the skies is a common aspiration for many. Becoming a pilot in India is not just about learning to fly; it’s a journey that demands dedication, skill, and persistence. For those starting from scratch, the roadmap to achieving the ultimate goal of airline entry involves structured steps, careful planning, and commitment. In this blog, we outline a detailed roadmap to help aspiring pilots navigate their way from zero to airline entry in India.
Step 1: Educational Foundation
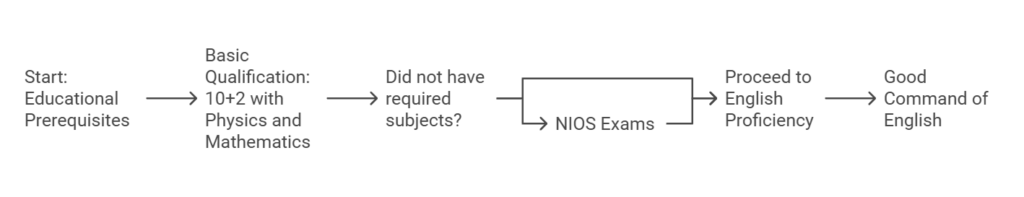
The first step in your pilot journey is meeting the educational requirements:
Basic Qualification: Completion of 10+2 with Physics and Mathematics is mandatory. If you didn’t have these subjects, you can appear for equivalent exams through the National Institute of Open Schooling (NIOS).
English Proficiency: A good command of English is essential as aviation communication primarily uses this language.
Step 2: Research and Planning
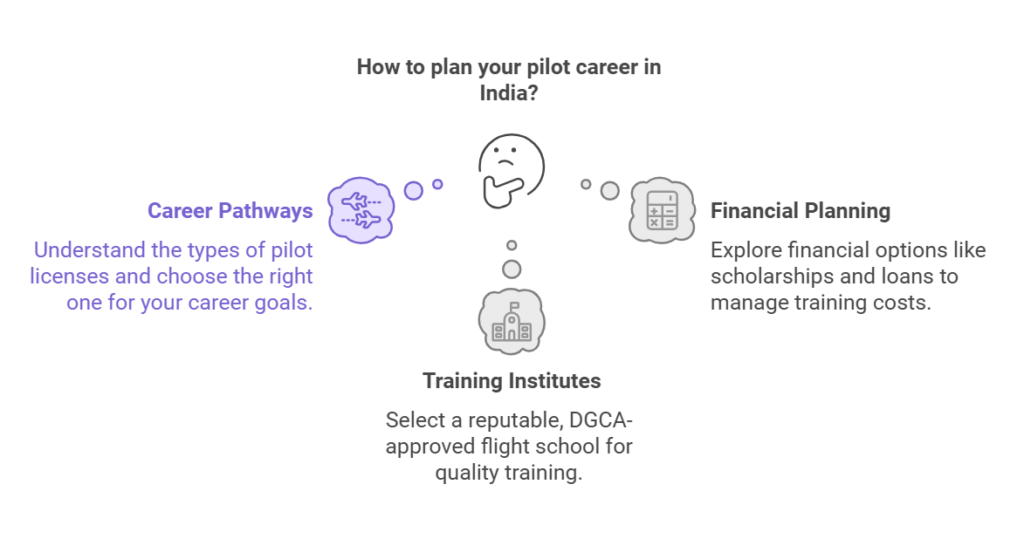
Before embarking on your pilot journey, it’s crucial to research:
Career Pathways: Understand the different types of pilot licenses—Private Pilot License (PPL), Commercial Pilot License (CPL), and Airline Transport Pilot License (ATPL).
Financial Planning: Pilot training is a significant investment. Costs can range from INR 35 – 50 lakhs for obtaining a CPL. Explore scholarships, bank loans, and sponsorships to manage finances.
Training Institutes: Choose a DGCA-approved flight school in India or abroad. Reputed institutes help students build lifelong foundations and skills that are necessary for student. At CFT we ensure these are incorporated from day 1.
Step 3: Medical Fitness
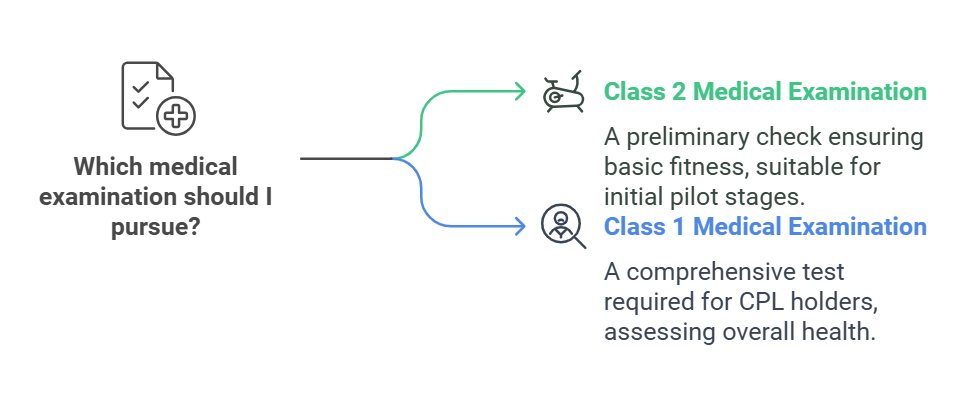
Medical fitness is non-negotiable for pilots. You must clear the following:
Class 2 Medical Examination: Conducted by DGCA-approved doctors. This is a preliminary check to ensure basic fitness.
Class 1 Medical Examination: A more comprehensive test required for CPL holders. It includes blood tests, vision, hearing, cardiovascular, and overall health assessments.
Maintaining good physical and mental health throughout your training is vital.
Step 4: Student Pilot License (SPL)
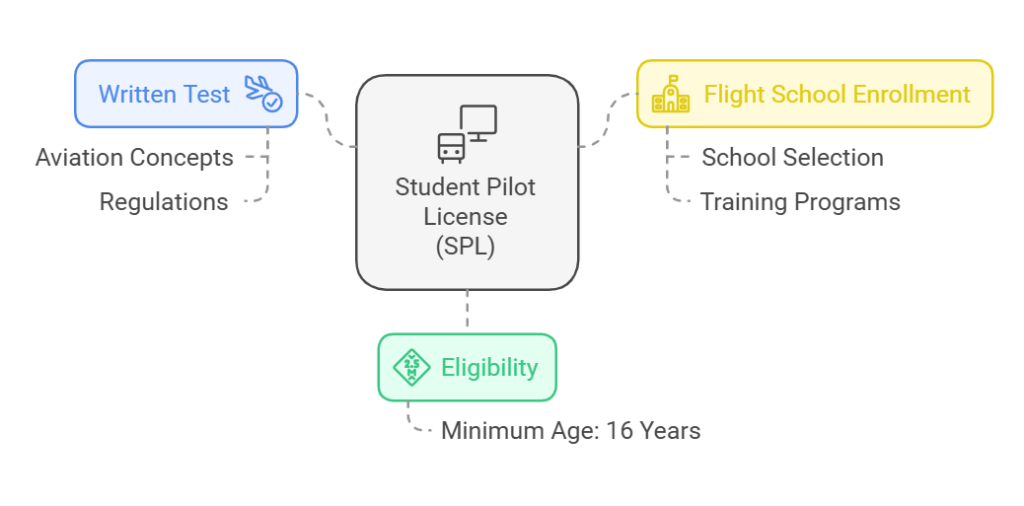
Your first step into practical flying begins with obtaining an SPL. This involves:
Eligibility: Minimum age of 16 years.
Written Test: Covers basic aviation concepts and rules.
Flight School Enrollment: Choose a school that provides SPL training.
The SPL allows you to start basic flight training under the supervision of an instructor.
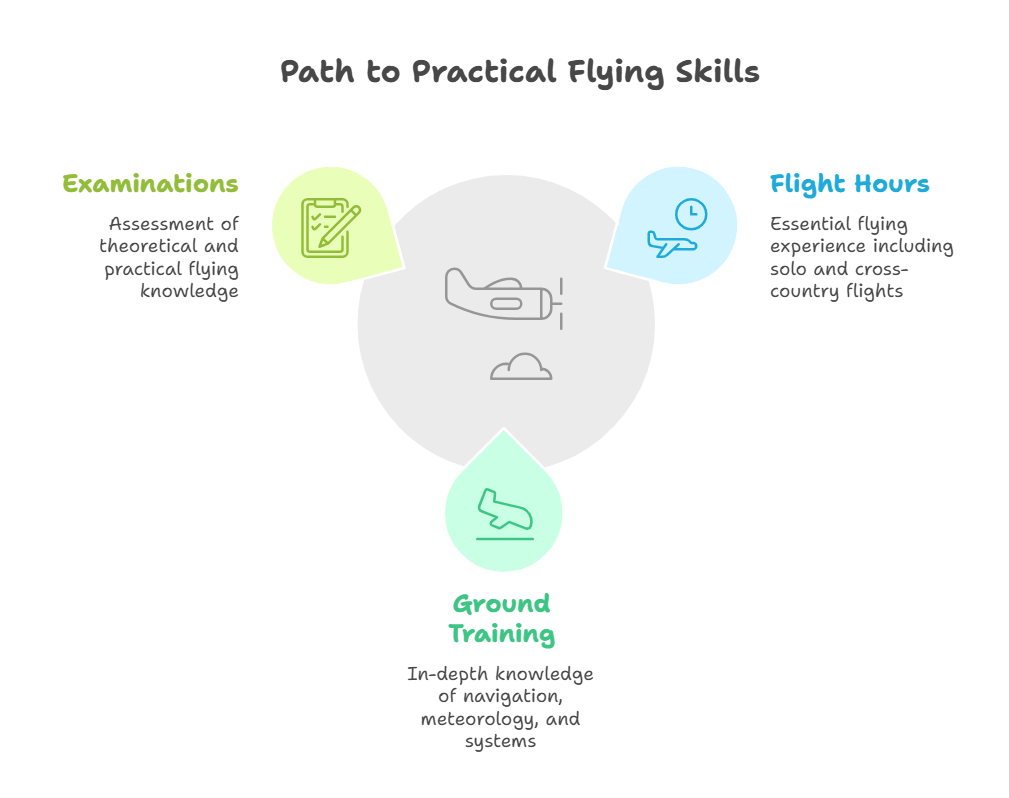
Step 5: Private Pilot License (PPL)
The PPL is the foundation of practical flying skills:
Flight Hours: A minimum of 40 flight hours, including solo flying and cross-country navigation.
Ground Training: Covers subjects like Air Navigation, Meteorology, and Aircraft Systems.
Examination: DGCA conducts both written and flying tests.
With a PPL, you can fly an aircraft for non-commercial purposes.
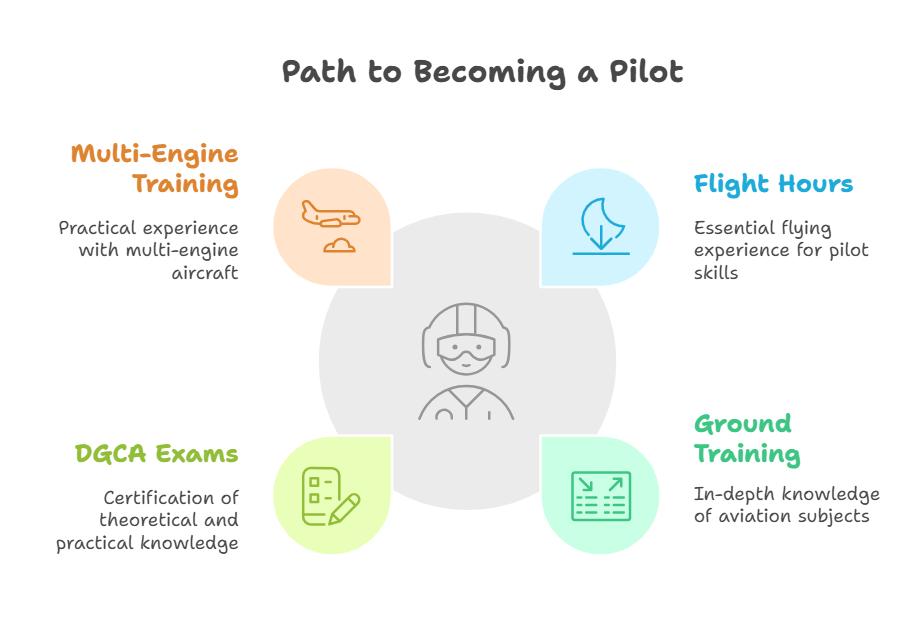
Step 6: Commercial Pilot License (CPL)
The CPL is the gateway to professional flying:
Flight Hours: Accumulate at least 200 flight hours, including night flying and instrument flying.
Ground Training: Comprehensive courses on Air Regulation, Meteorology, Air Navigation, and Technical General.
DGCA Exams: Clearing the DGCA’s written and oral exams is mandatory.
Multi-Engine Training: Experience flying multi-engine aircraft, essential for airline operations.
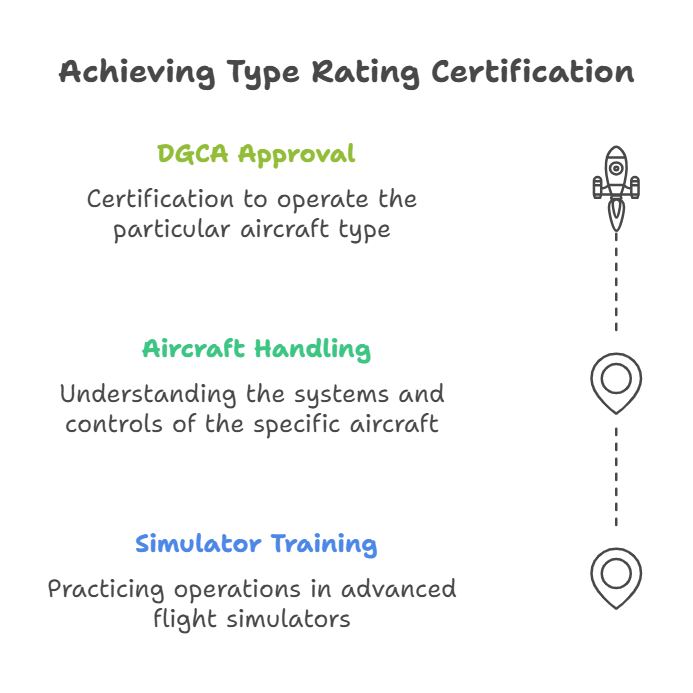
Step 7: Type Rating
Type Rating is specialized training for a specific aircraft model, such as Airbus A320 or Boeing 737. It includes:
Simulator Training: Practicing operations in advanced flight simulators.
Aircraft Handling: Understanding the systems and controls of the specific aircraft.
DGCA Approval: Certification to operate the particular aircraft type.
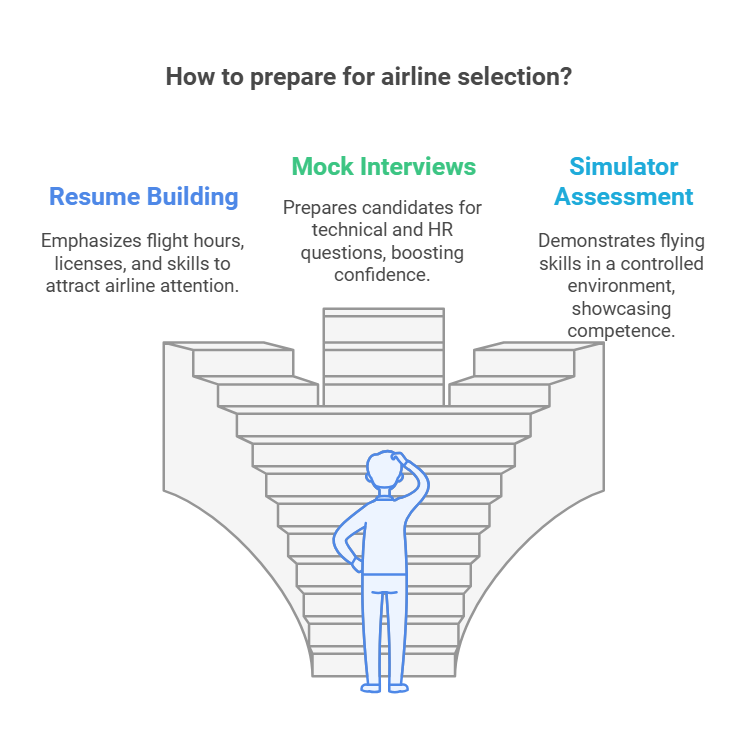
Step 8: Airline Preparations
Preparing for airline selection involves:
Resume Building: Highlight your flight hours, licenses, and skills.
Mock Interviews: Practice technical and HR interviews conducted by airlines.
Simulator Assessment: Showcase your flying skills in a simulated environment.
Psychometric Tests: Assess your decision-making, problem-solving, and teamwork abilities.
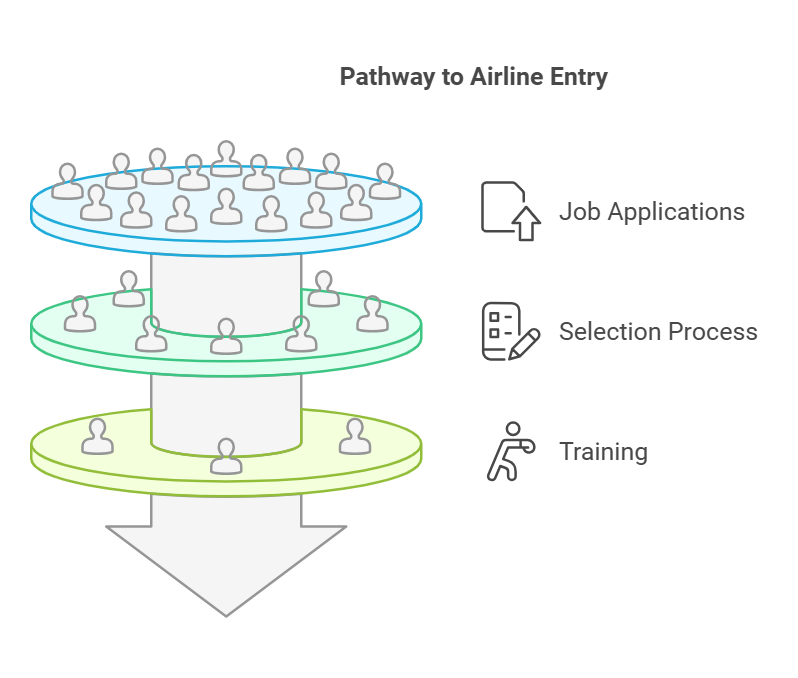
Step 9: Airline Entry
Securing a position with an airline is the ultimate goal. The process includes:
Job Applications: Apply to airlines actively hiring cadet pilots or junior first officers.
Selection Process: Airlines conduct written tests, interviews, and simulator checks.
Training: Selected candidates undergo airline-specific training before beginning operational duties.
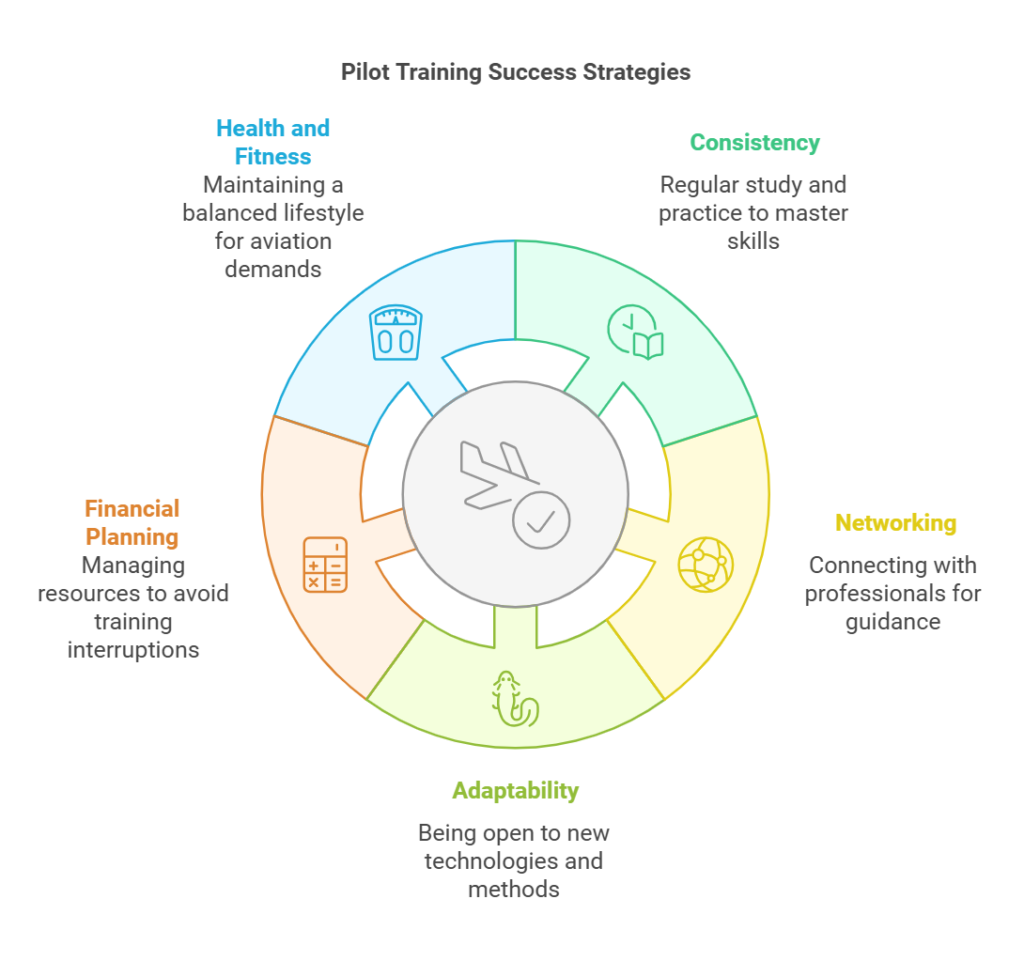
Tips for Success
Consistency: Regular study and practice are key to mastering theoretical and practical skills.
Networking: Connect with industry professionals and peers for guidance and opportunities.
Adaptability: Be open to learning and adapting to new technologies and methods.
Financial Planning: Manage resources wisely to avoid interruptions in training.
Health and Fitness: Maintain a balanced lifestyle to meet the demanding requirements of aviation.
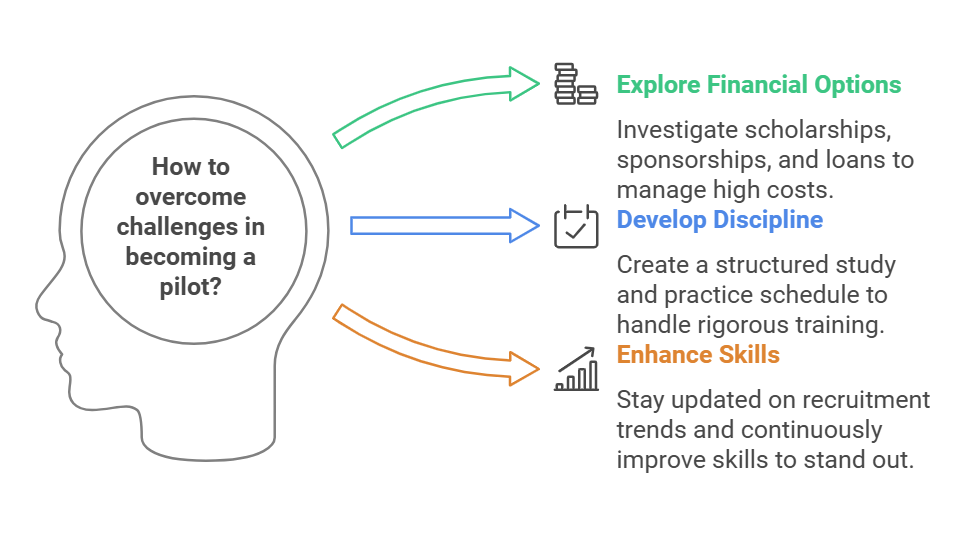
Challenges and How to Overcome Them
High Costs: Explore scholarships, sponsorships, and education loans.
Rigorous Training: Develop a disciplined approach to studying and practicing.
Competitive Selection: Stay updated on airline recruitment trends and enhance your skills continuously.
Conclusion
Becoming a pilot in India is a journey filled with challenges and rewards. From obtaining your first license to joining a commercial airline, each step is crucial in shaping your aviation career. At CFT, we are committed to helping aspiring pilots achieve their dreams through comprehensive training, expert guidance, and unwavering support. Start your journey with us today and take to the skies with confidence!
